January 14 2003
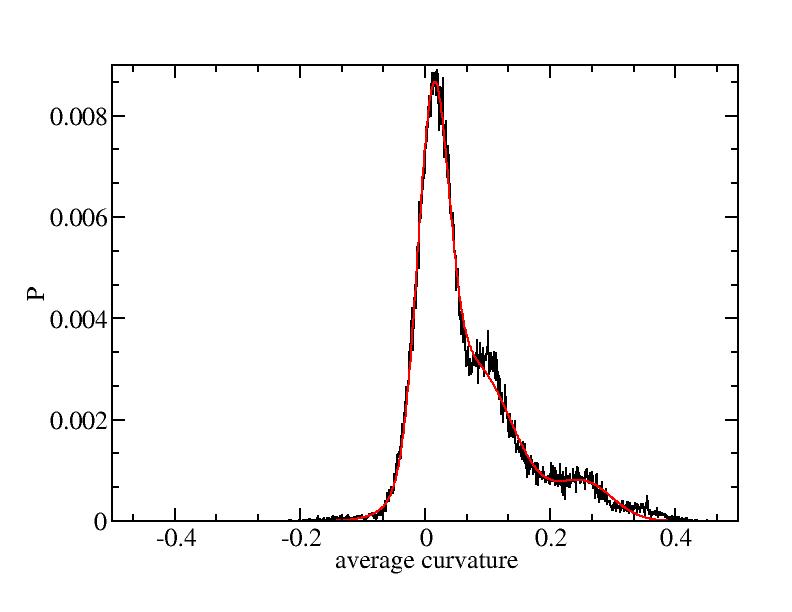
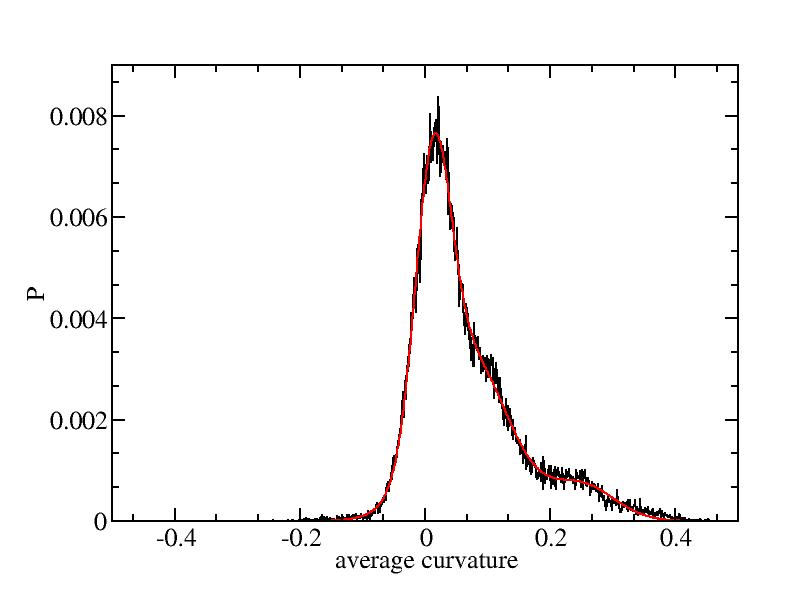
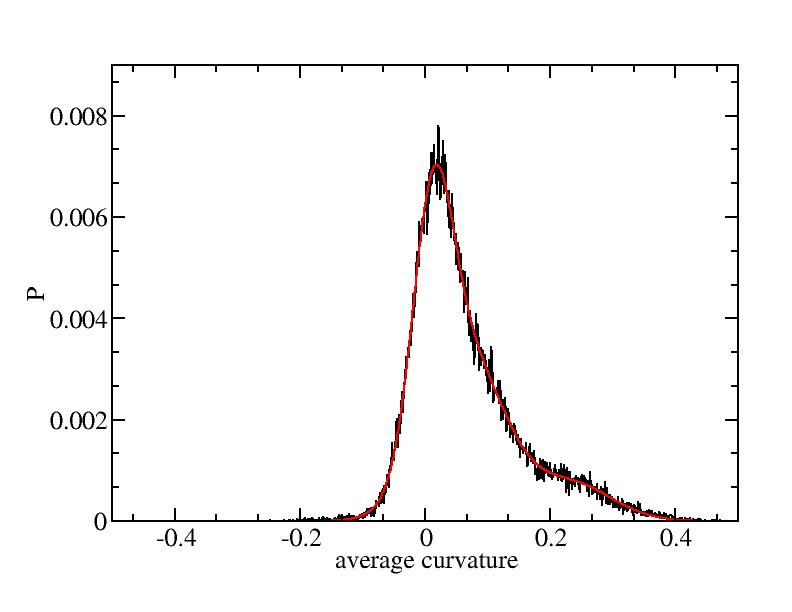
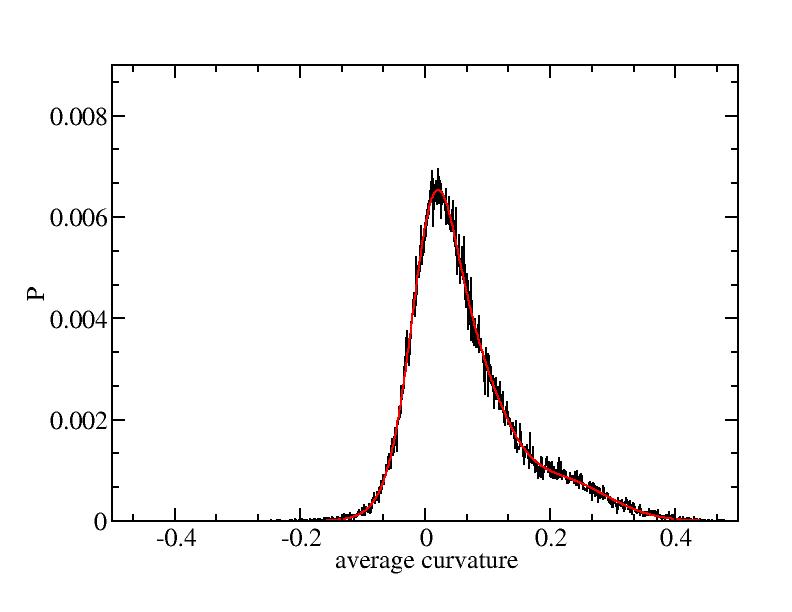
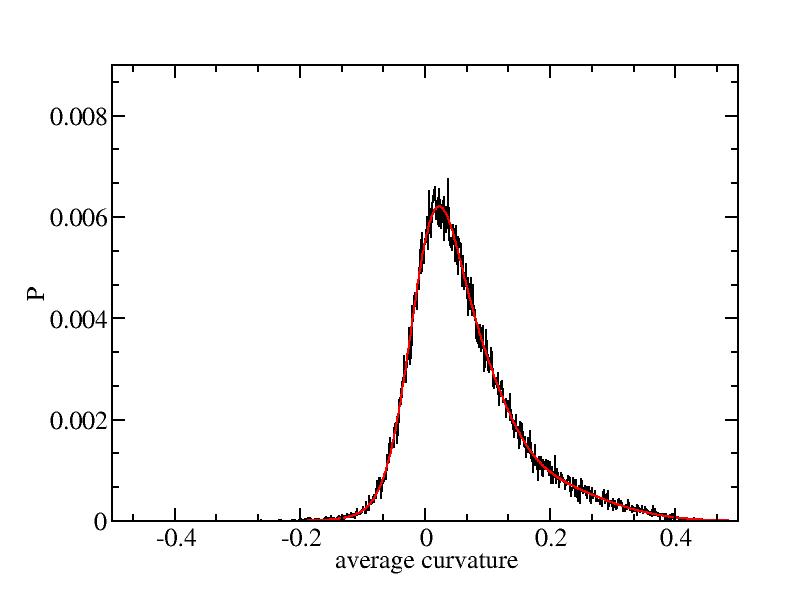
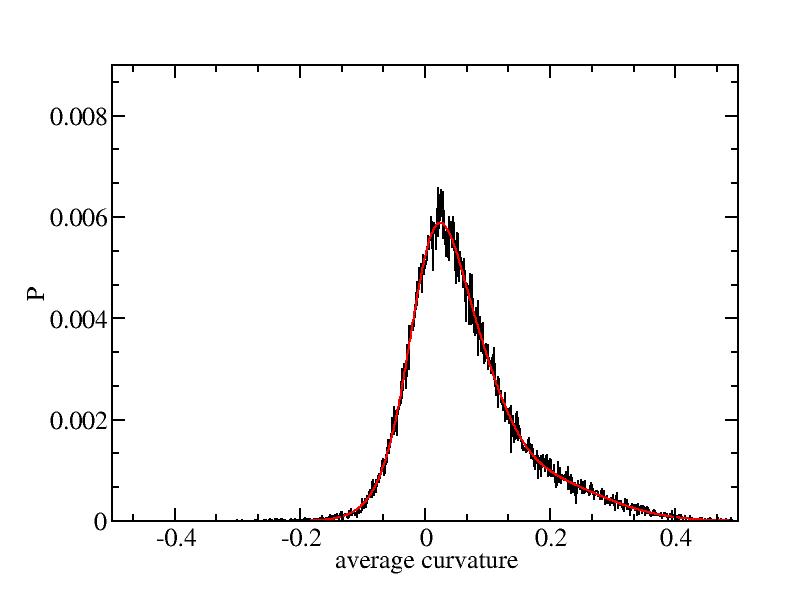
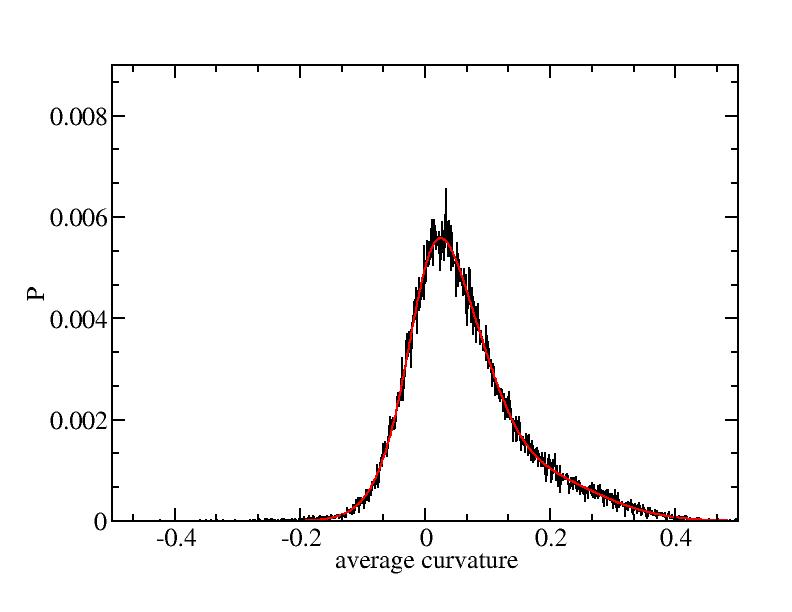
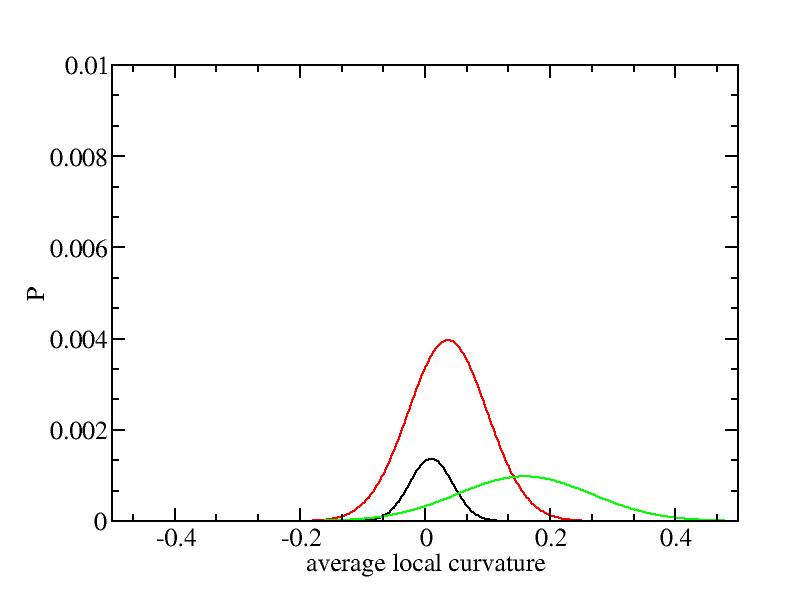
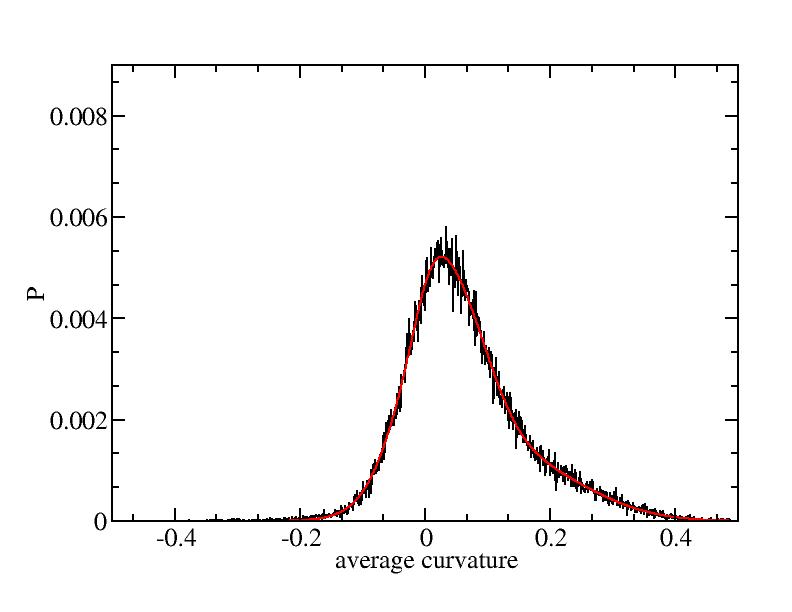
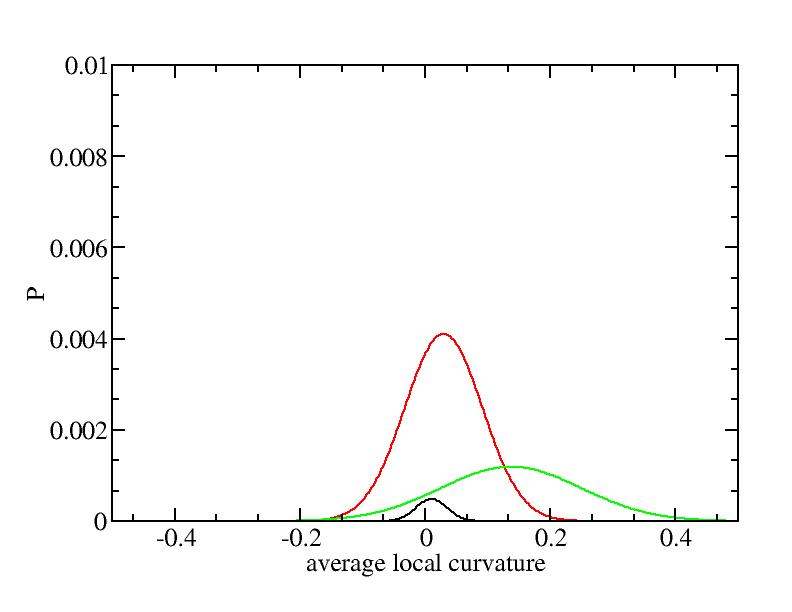
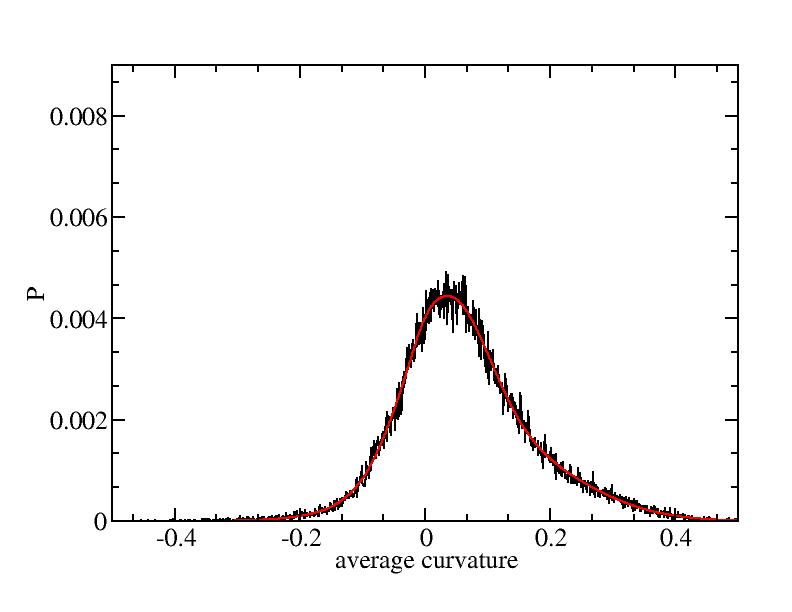
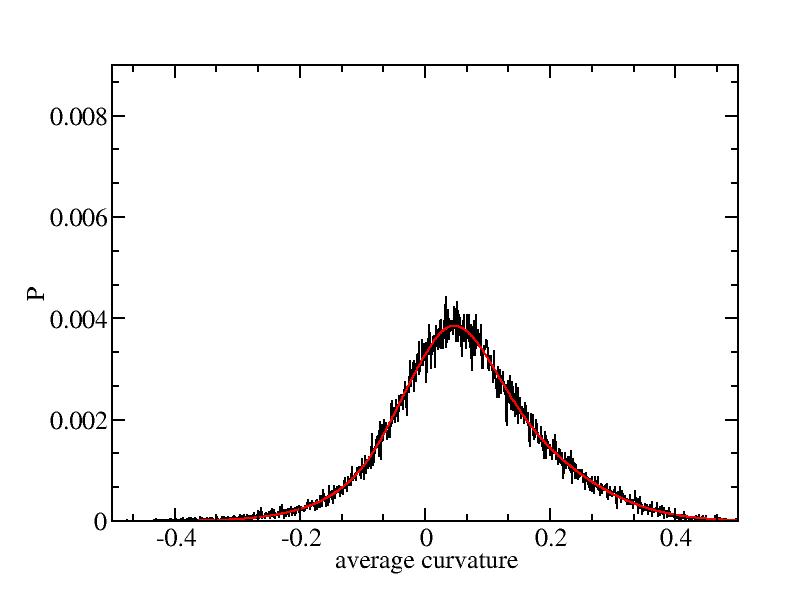
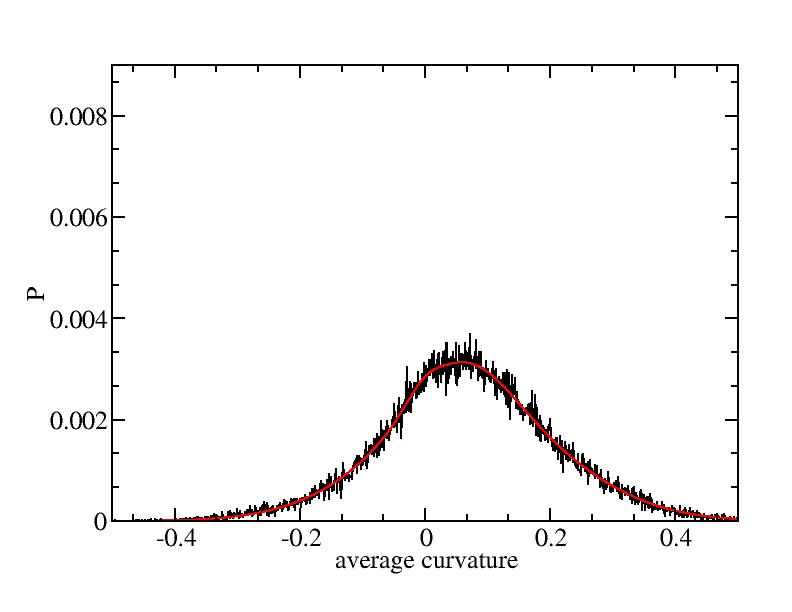
Fit average curvatures with Gaussian distributions (1409 atoms)
The sum of three Gaussian distributions have been used to fit the average
curvature distributions. The fitting Gaussian distribution function is
given as:
f = a0 / sigma * exp( - ( x - <x> )^2 / 2 / sigma^2 )
Because the integral of the density function is 1 (here with a factor of
1/sqrt(2*PI)), a0 is the fraction of the peak, which is propotional to number
of particles.
The peak value
p = f ( <x> ) = a0 / sigma
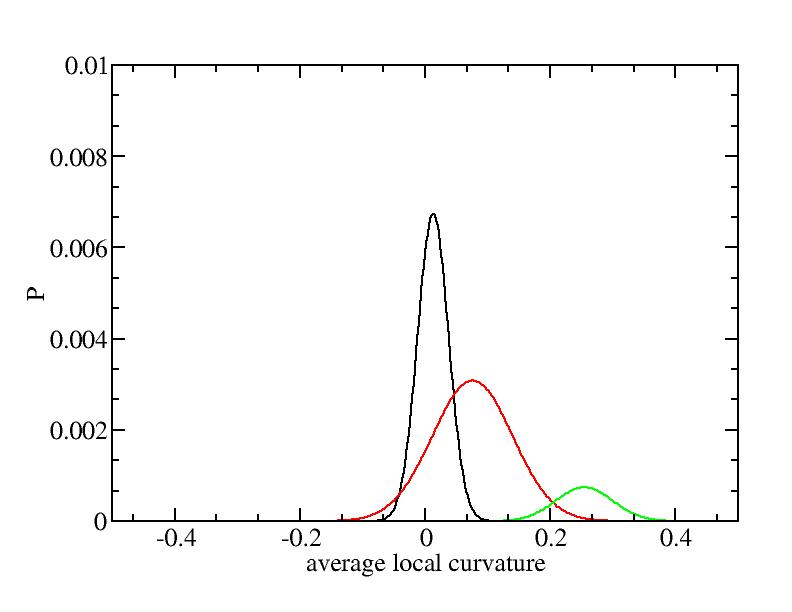
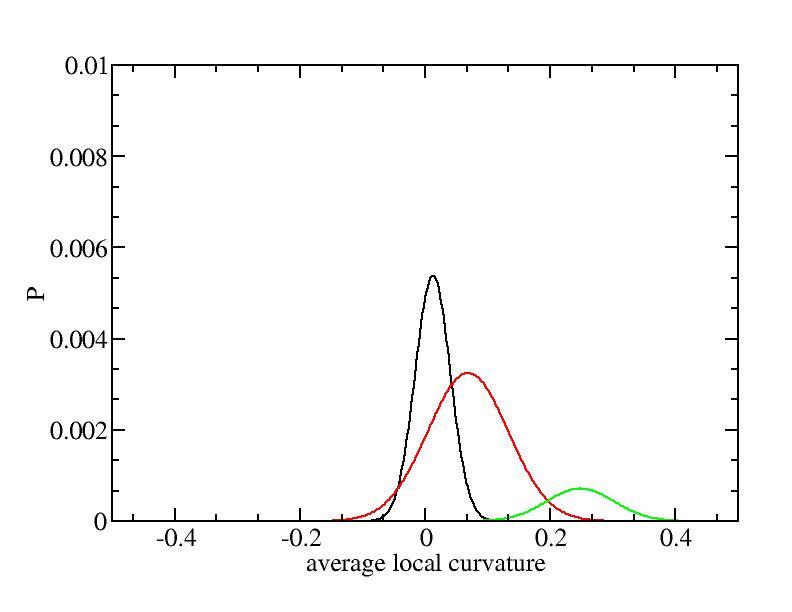
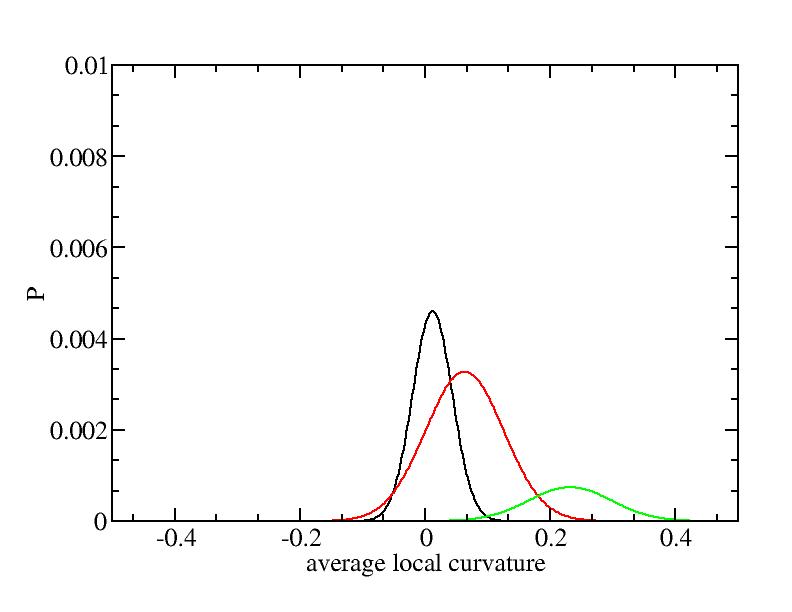
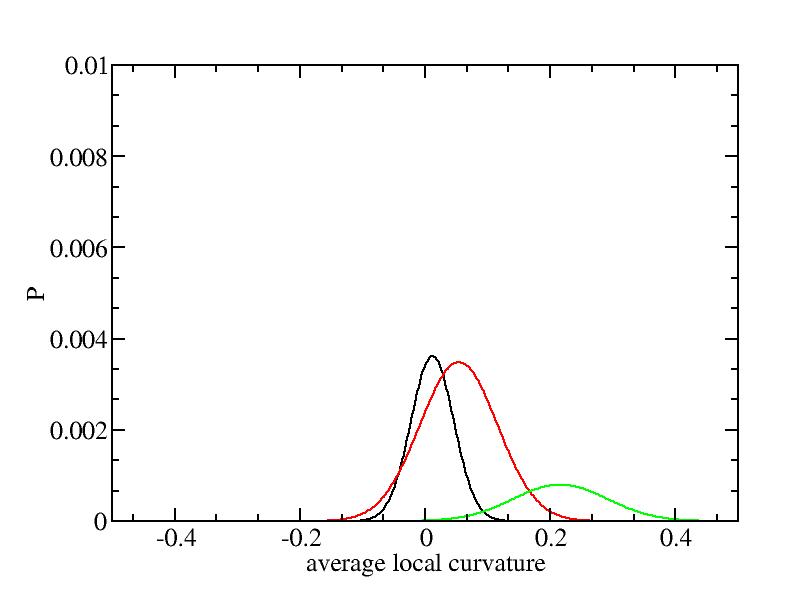
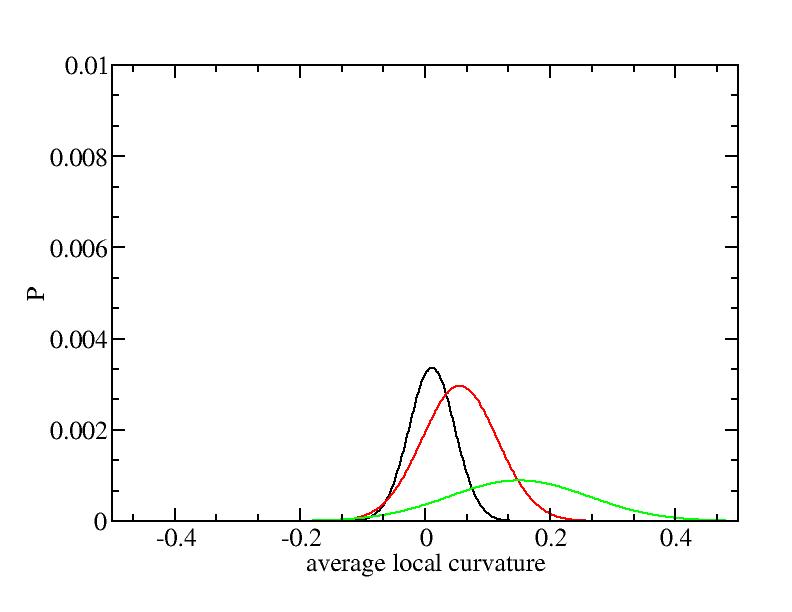
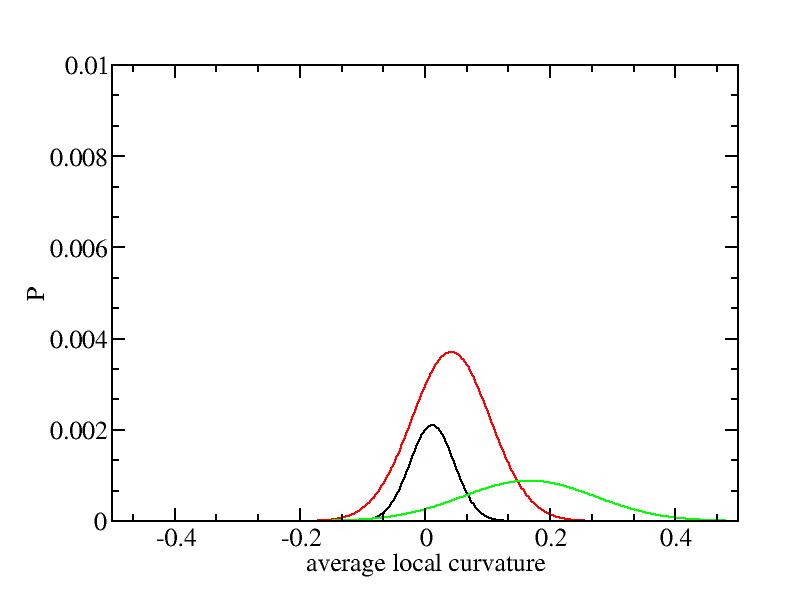
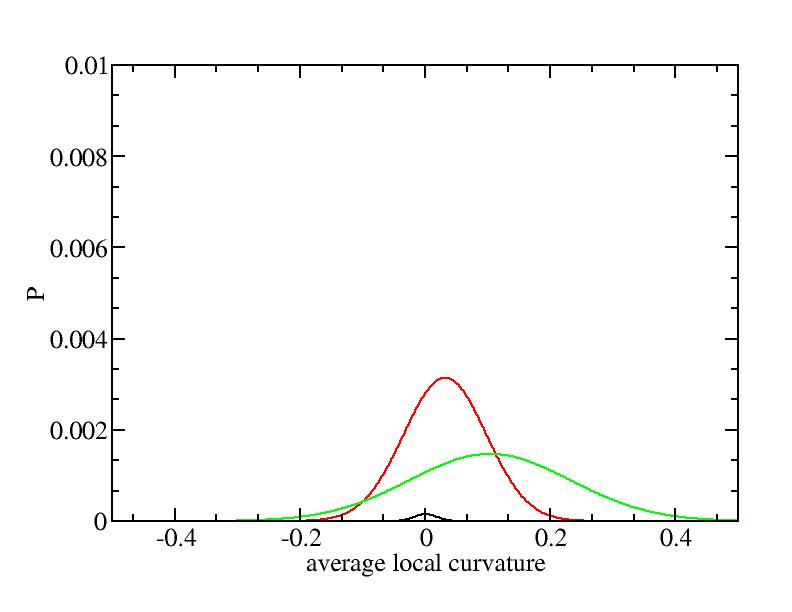
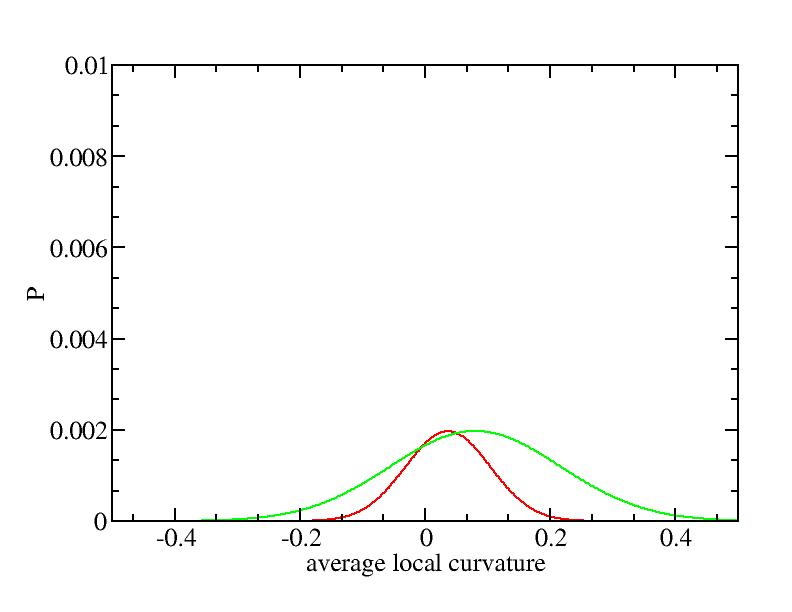
For each Gaussian peak, there are three independent parameters:
(p, sigma, <x>) or (a0, sigma, $lt;x>).
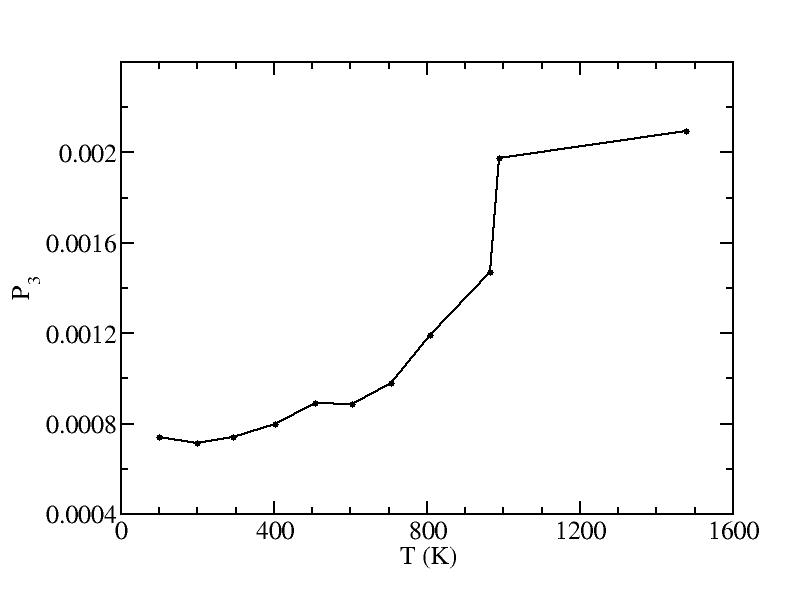
Fraction of a0
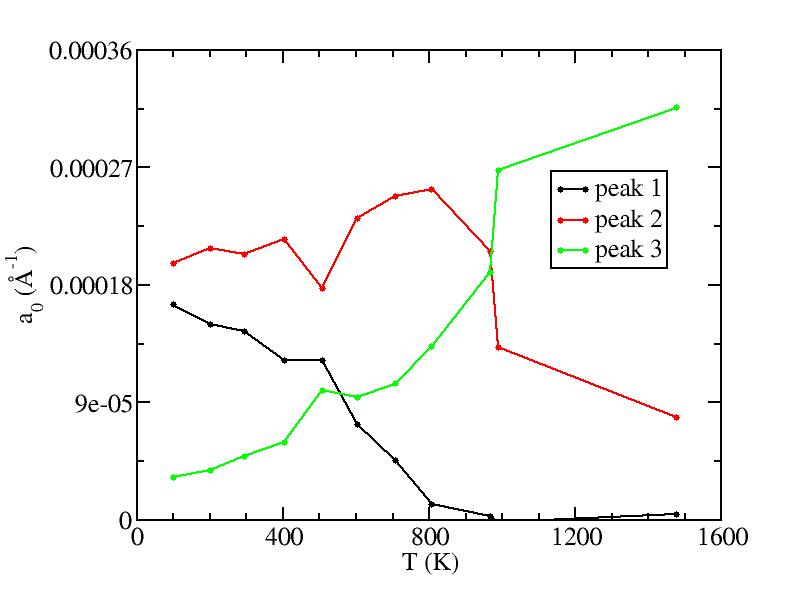
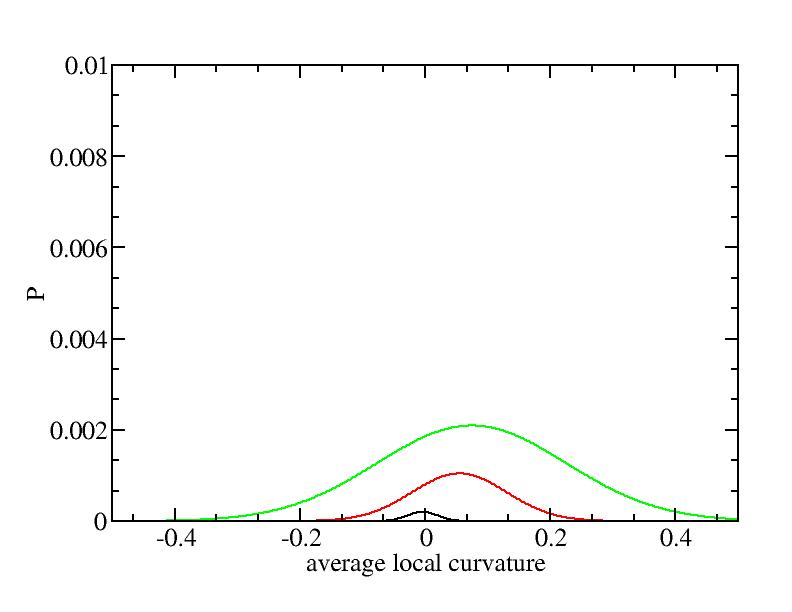
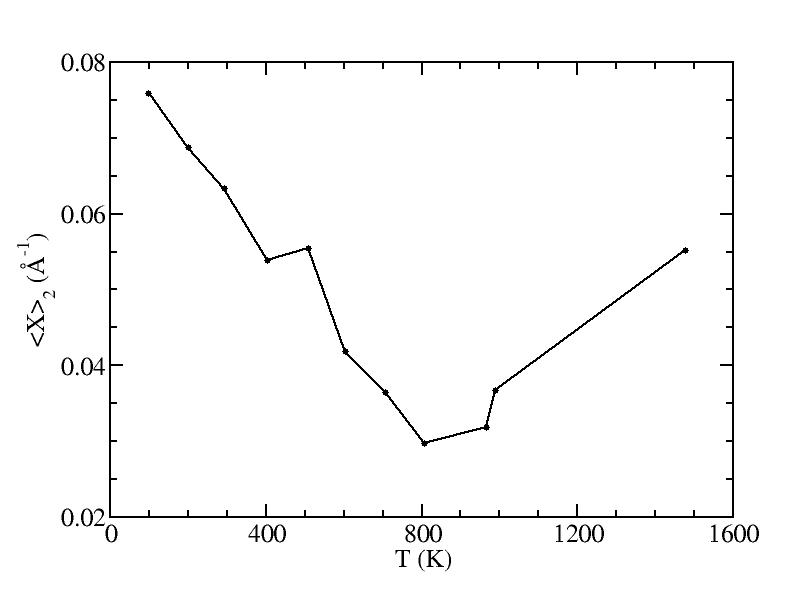
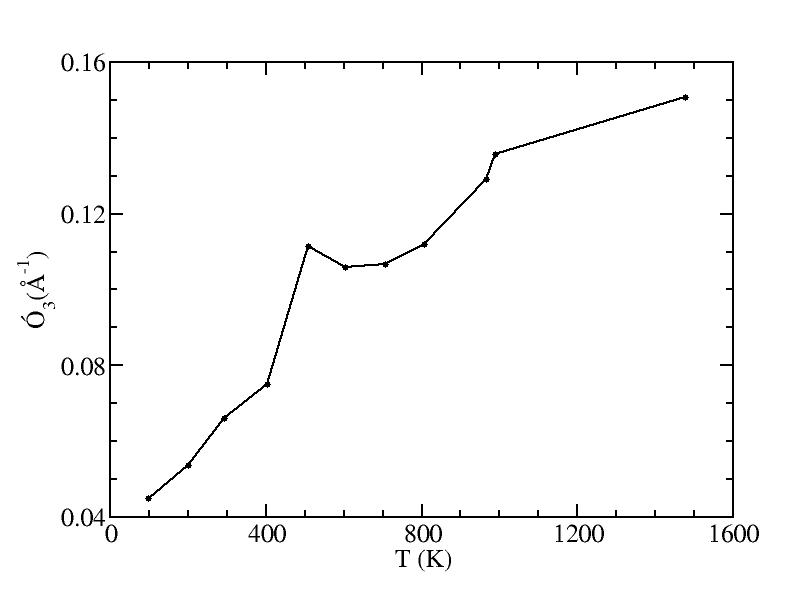
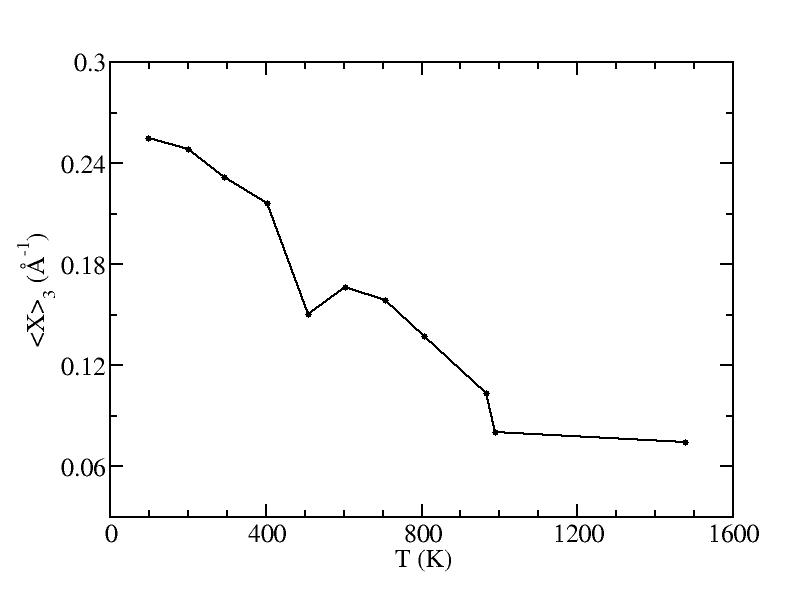
Parameters of three Gaussian peaks
| |
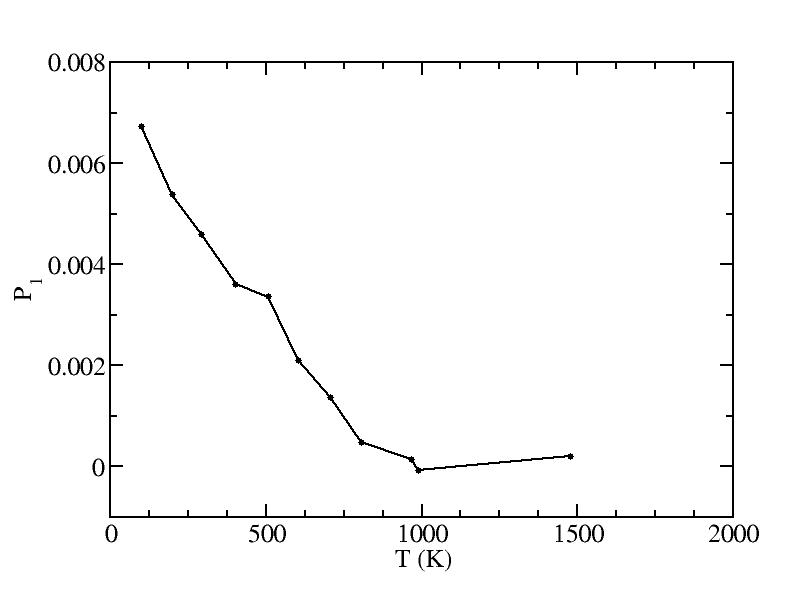
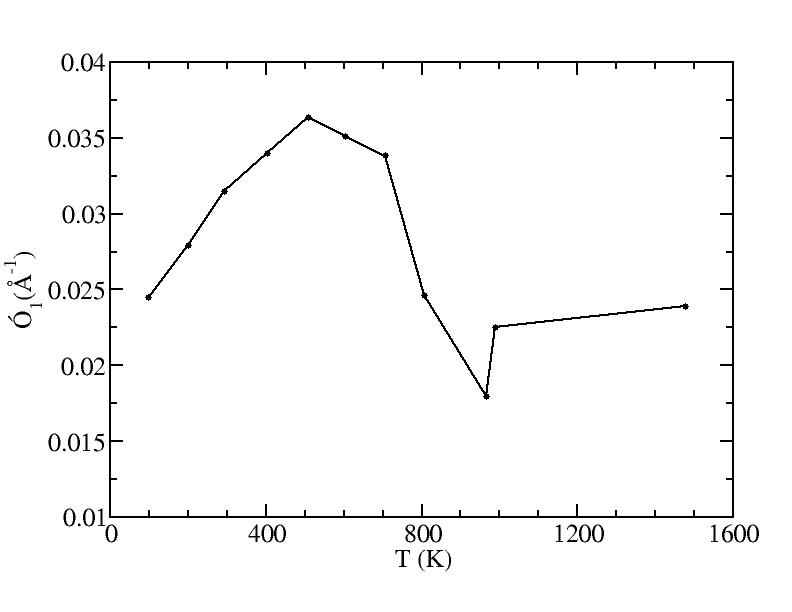
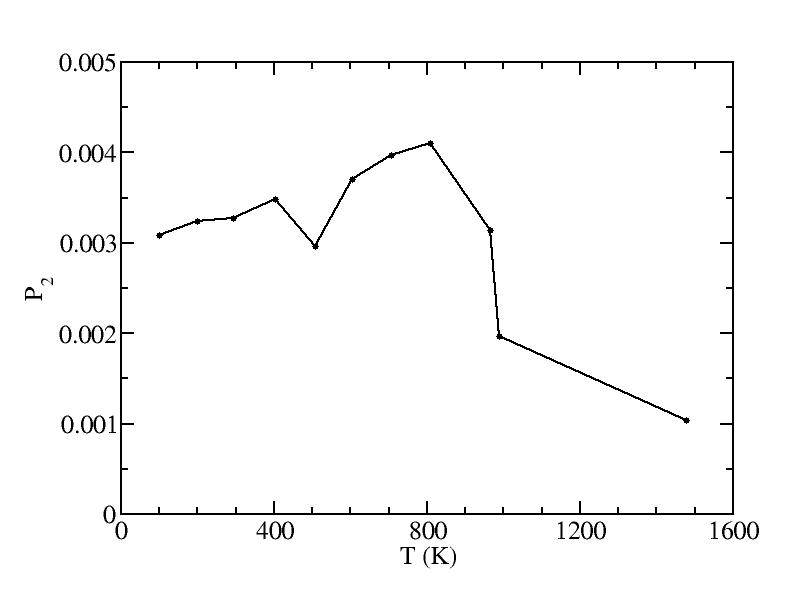
p
|
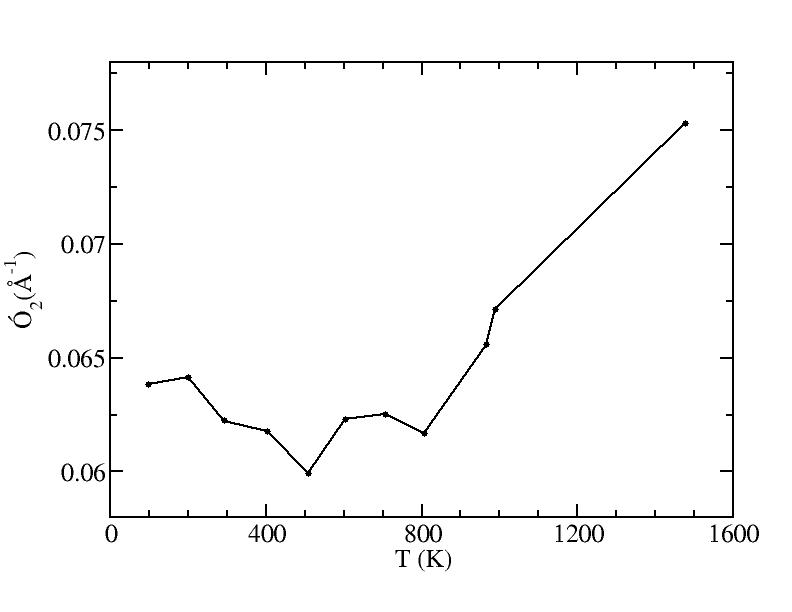
sigma
|
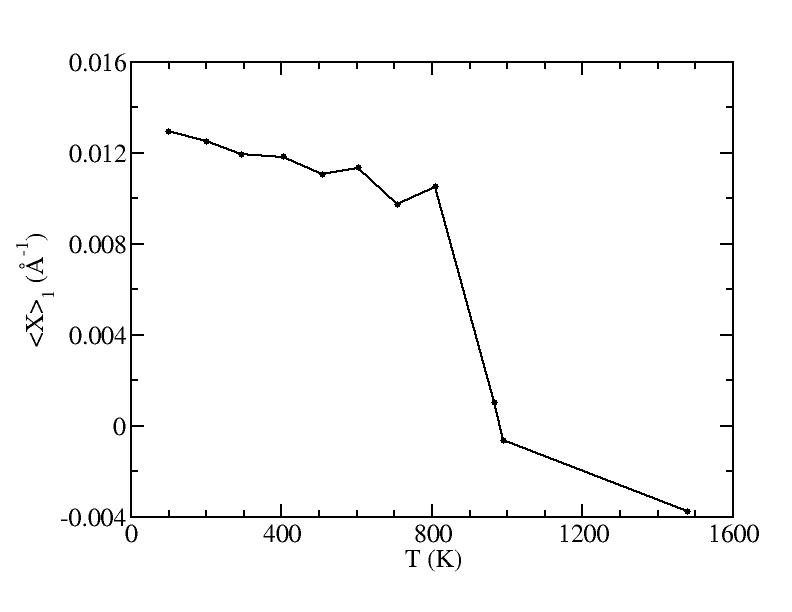
<x>
|
|
Peak 1
|
|
|
|
|
Peak 2
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Peak 3
|
 |
 |
 |
99K
200K
293K
403K
508K
603K
706K
807K
966K
989K
1478K