January 15 2003
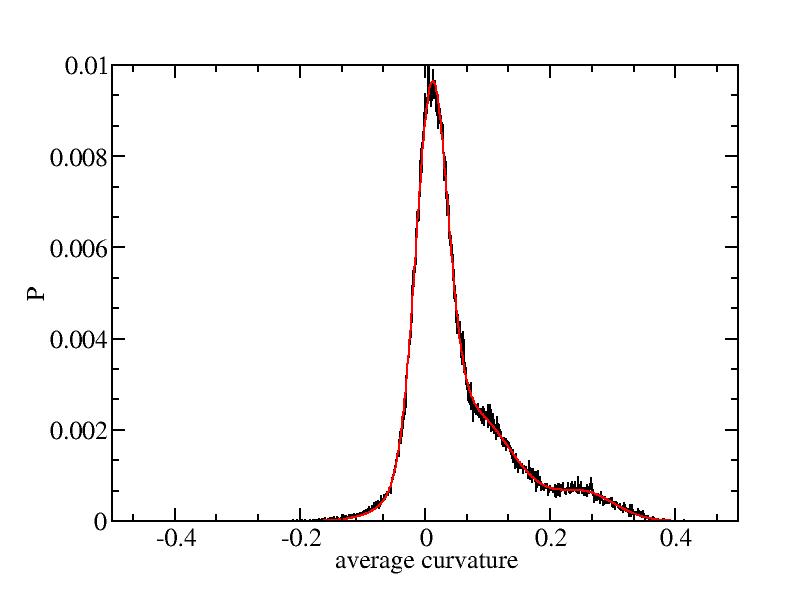
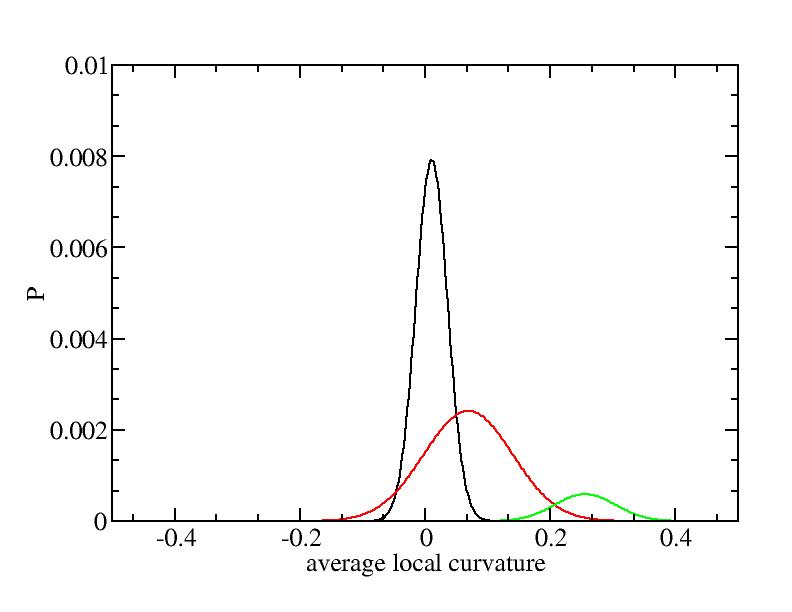
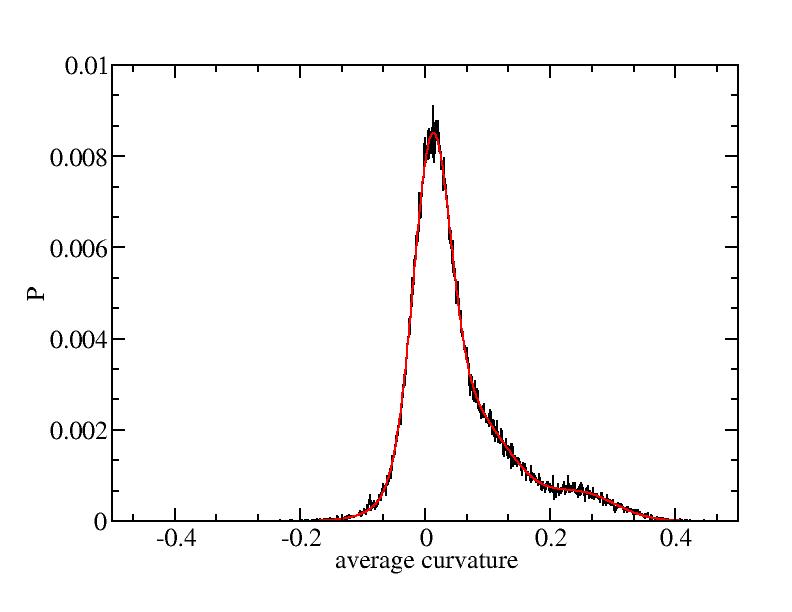
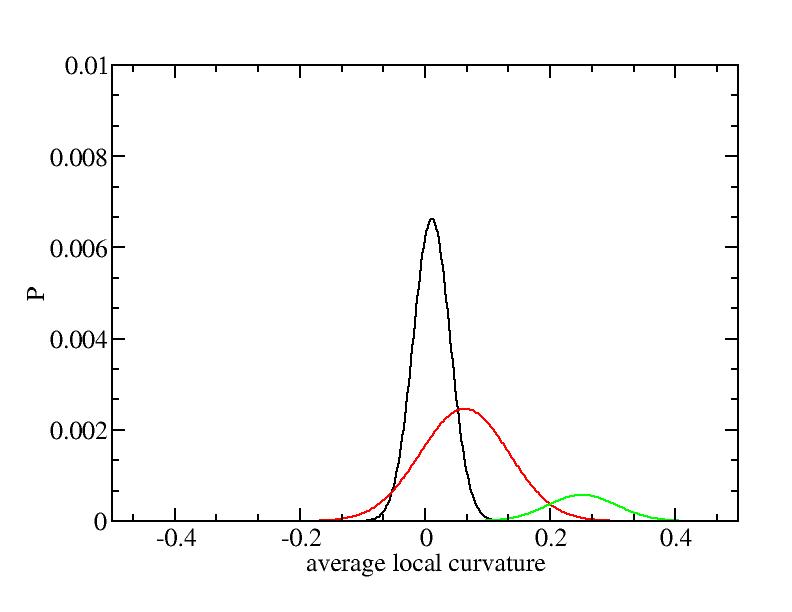
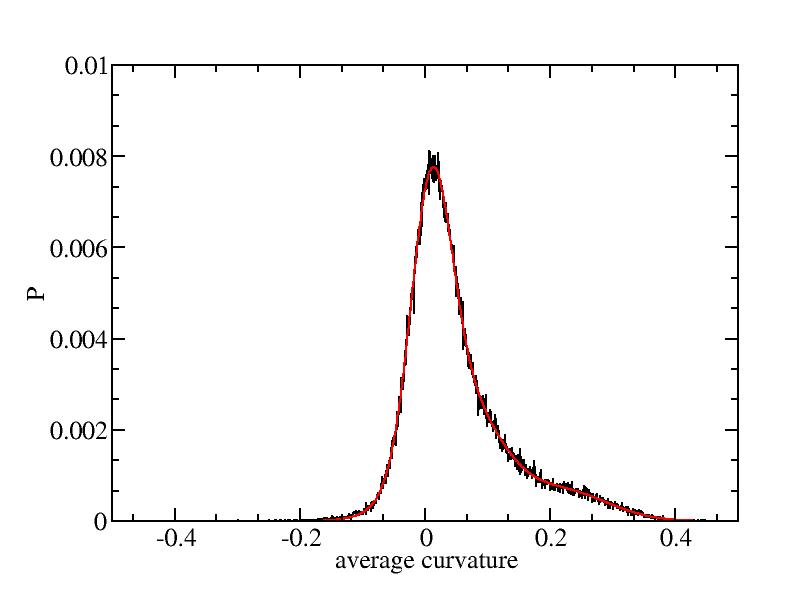
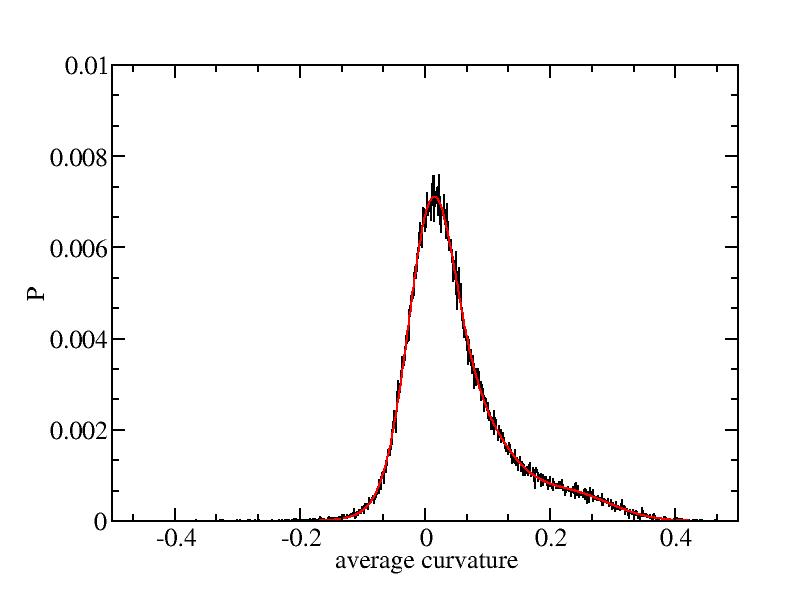
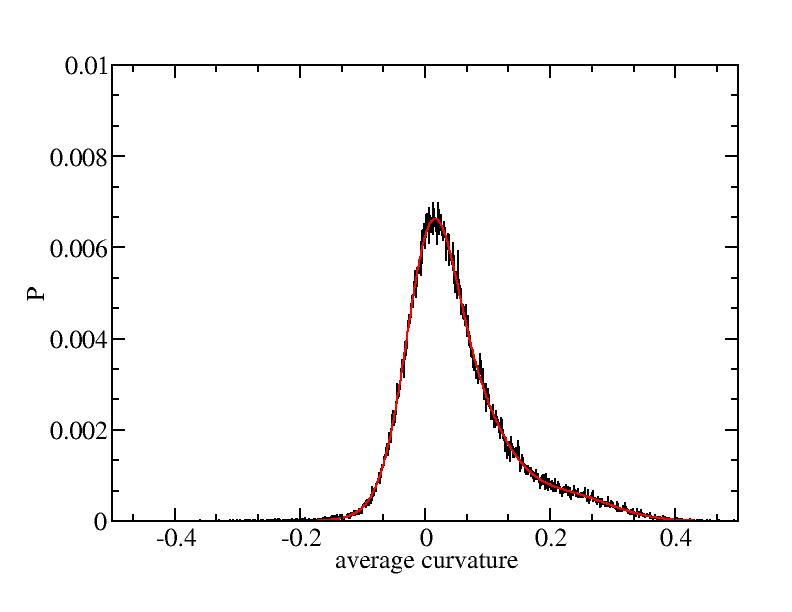
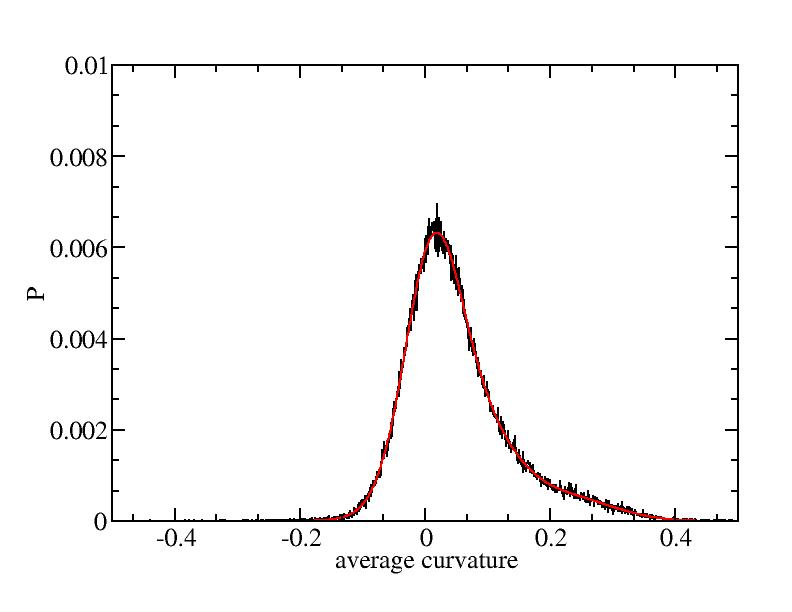
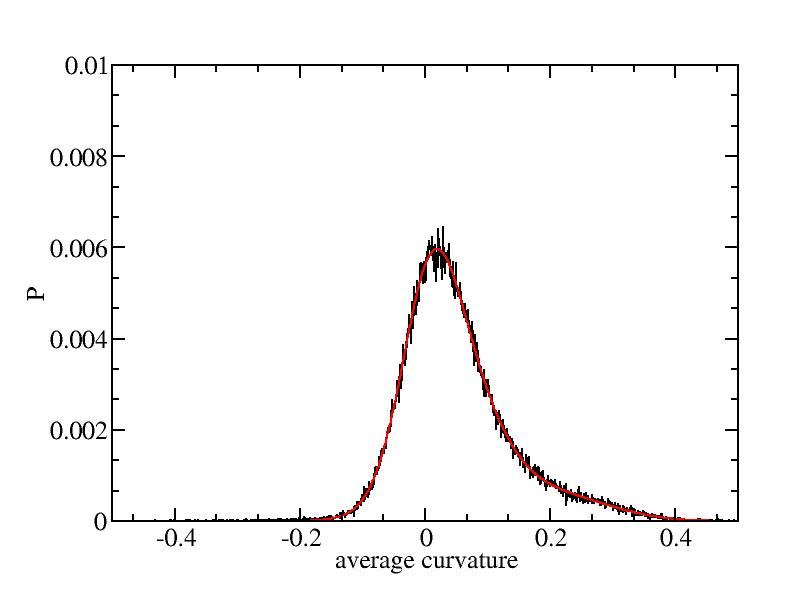
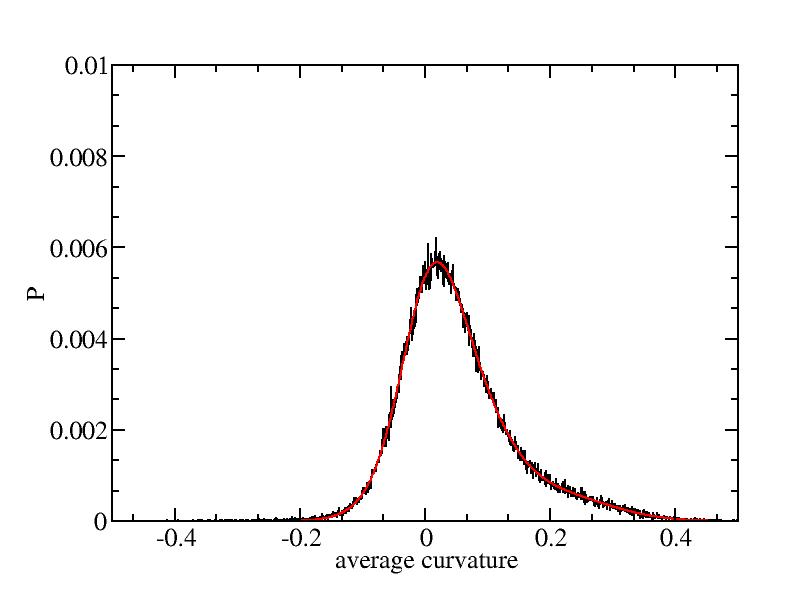
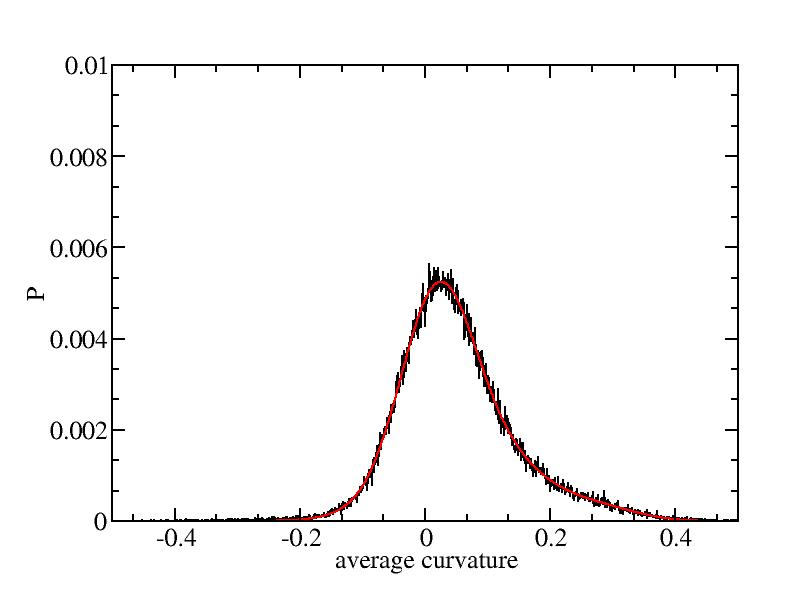
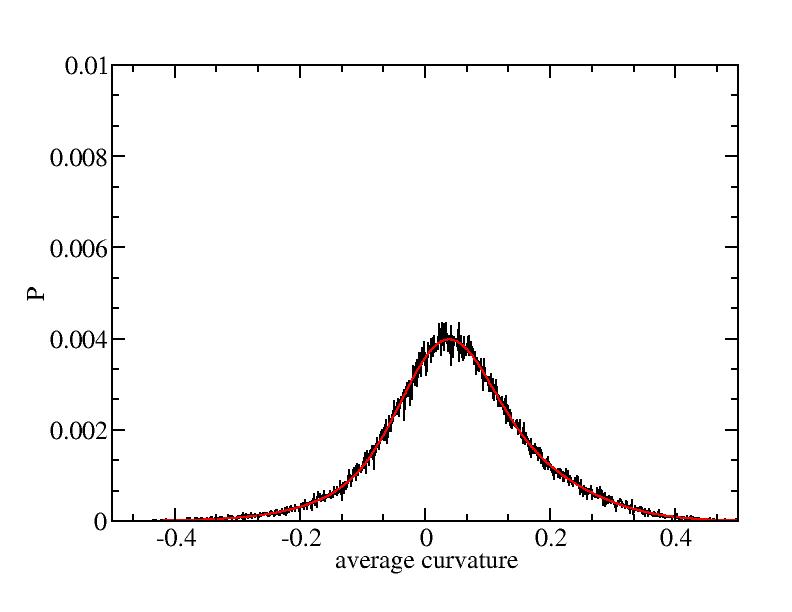
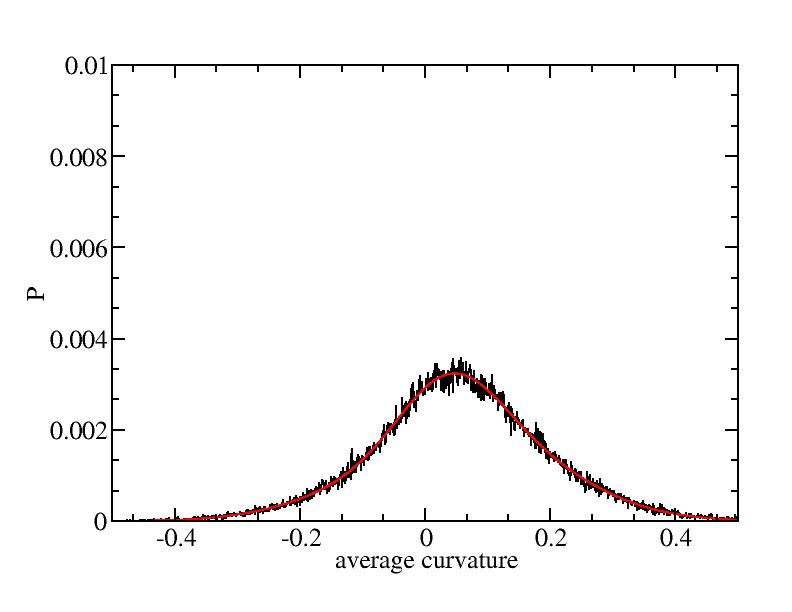
Fit average curvatures with Gaussian distributions (2624 atoms)
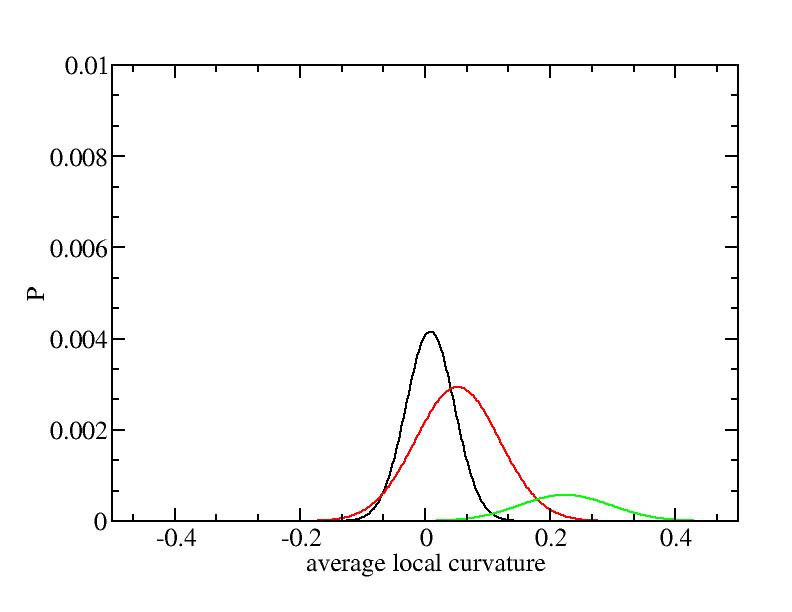
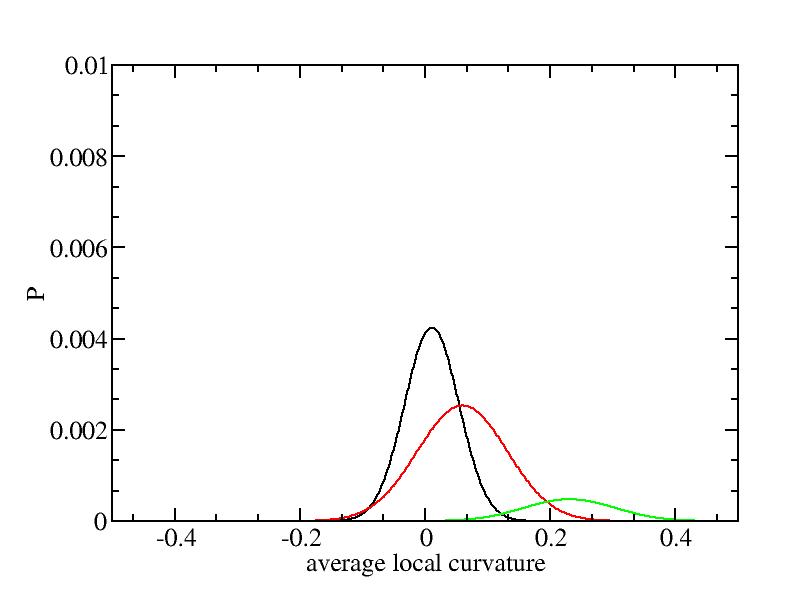
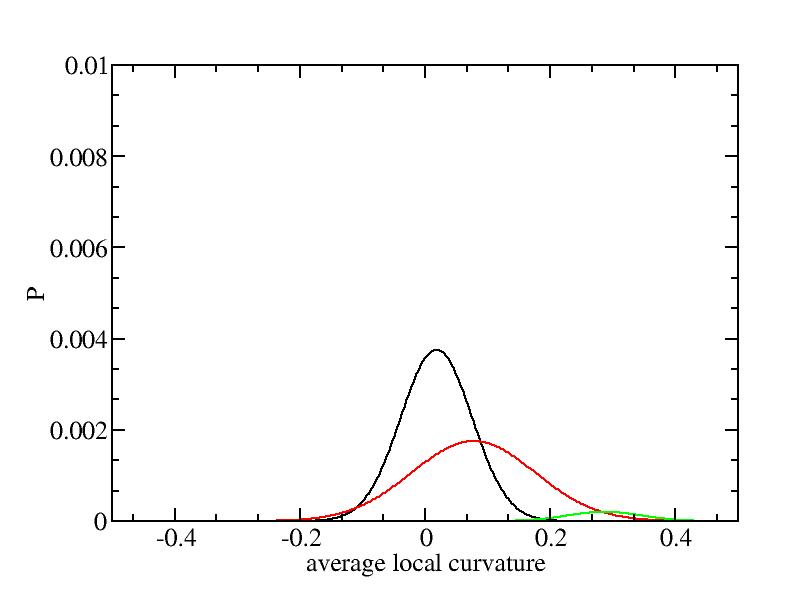
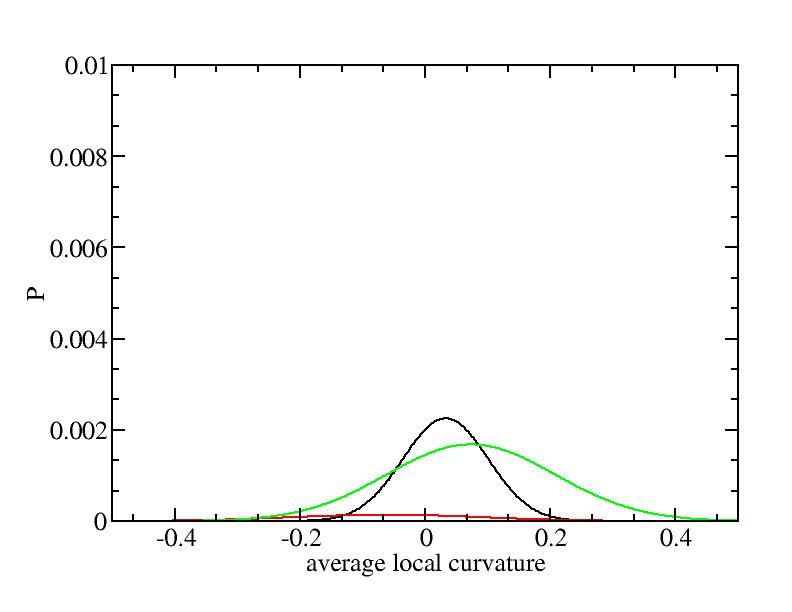
The sum of three Gaussian distributions have been used to fit the average
( (smaller+larger)/2 ) curvature distributions.
The fitting Gaussian distribution function is given as:
f = a0 / sigma * exp( - ( x - <x> )^2 / 2 / sigma^2 )
Because the integral of the density function is 1 (here with a factor of
1/sqrt(2*PI)), a0 is the fraction of the peak, which is propotional to number
of particles.
The peak value
p = f ( <x> ) = a0 / sigma
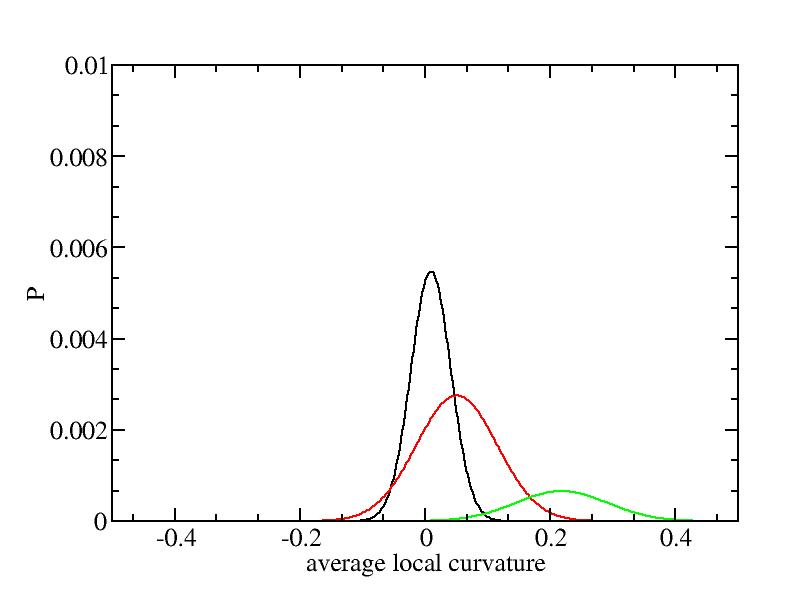
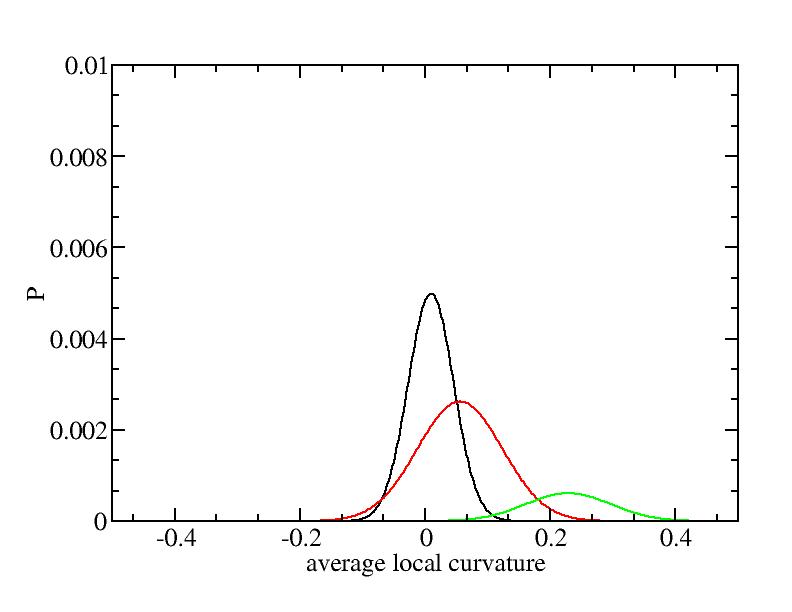
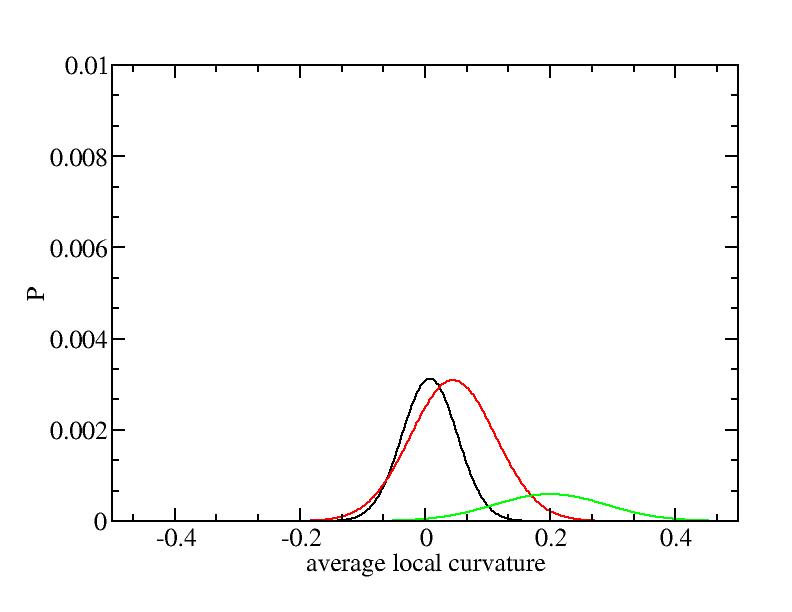
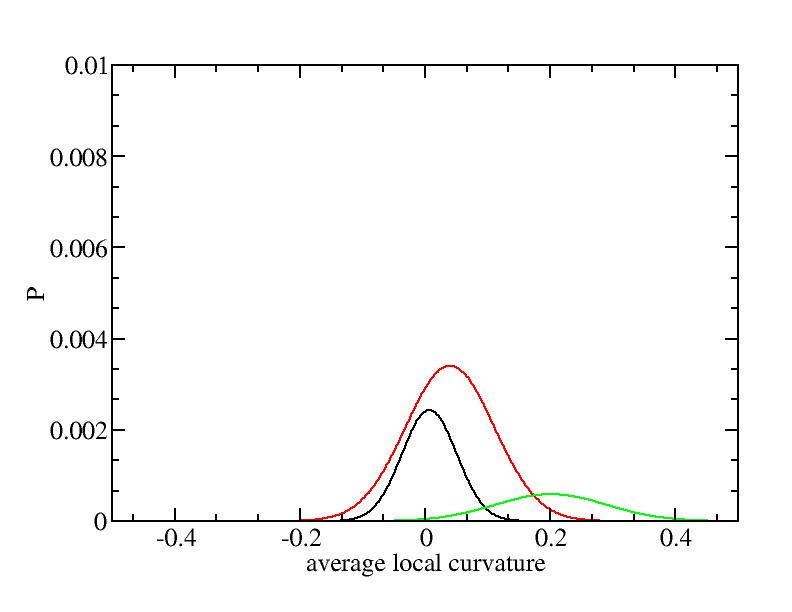
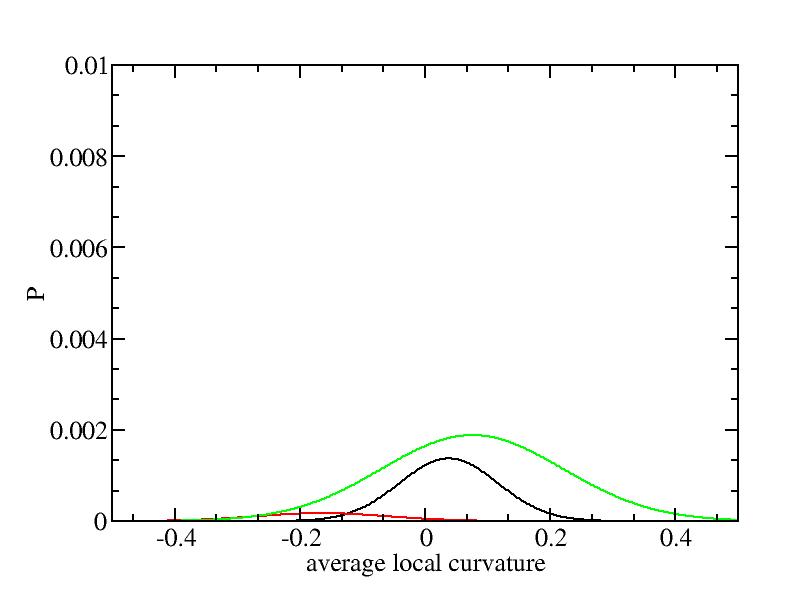
For each Gaussian peak, there are three independent parameters:
(p, sigma, <x>) or (a0, sigma, $lt;x>).
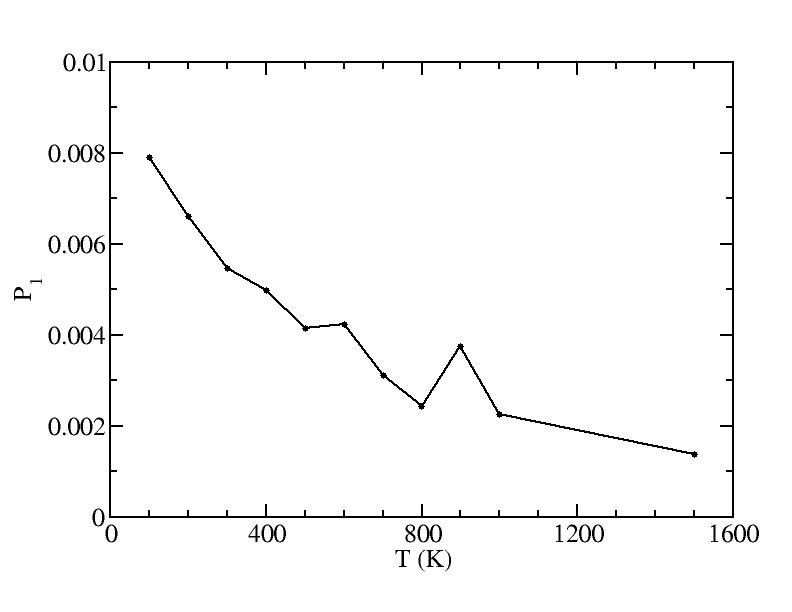
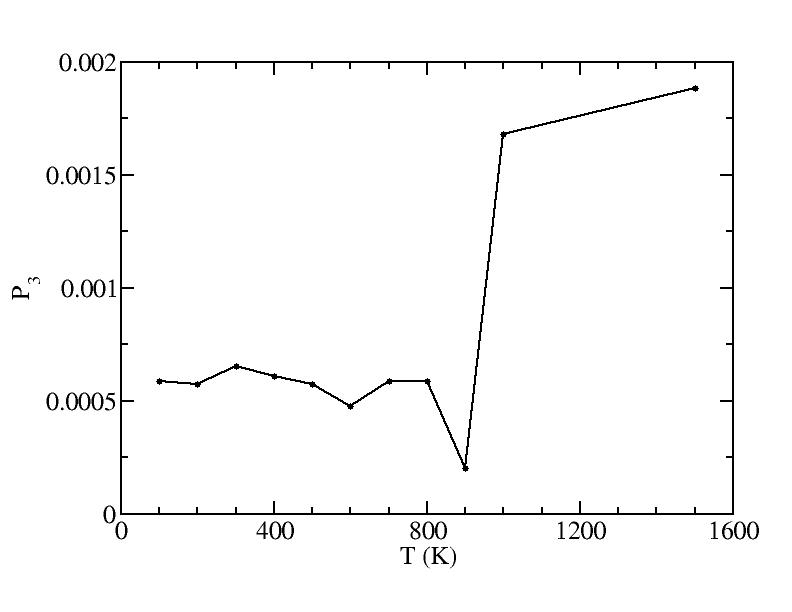
Fraction of a0
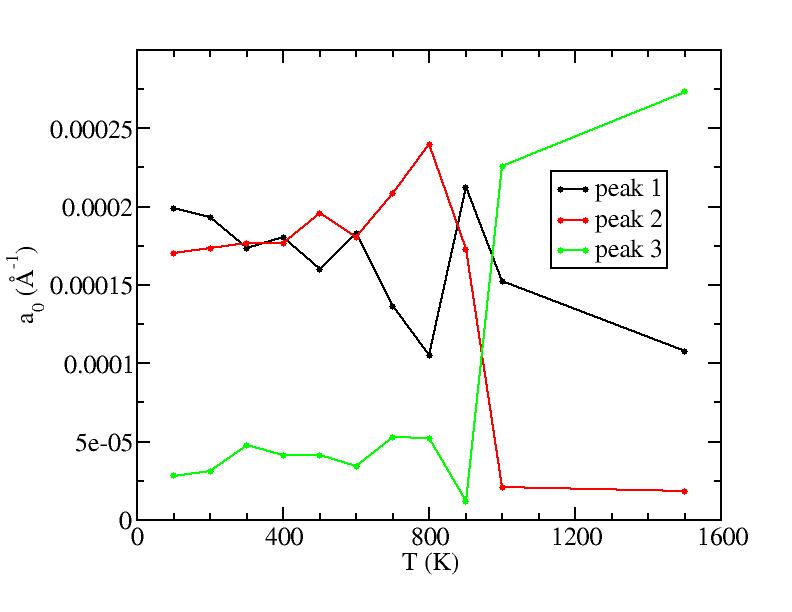
Parameters of three Gaussian peaks
| |
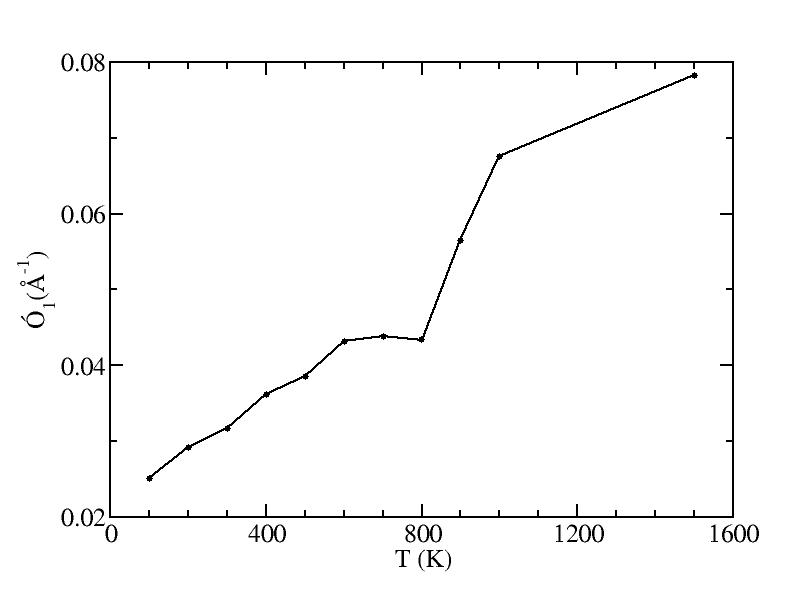
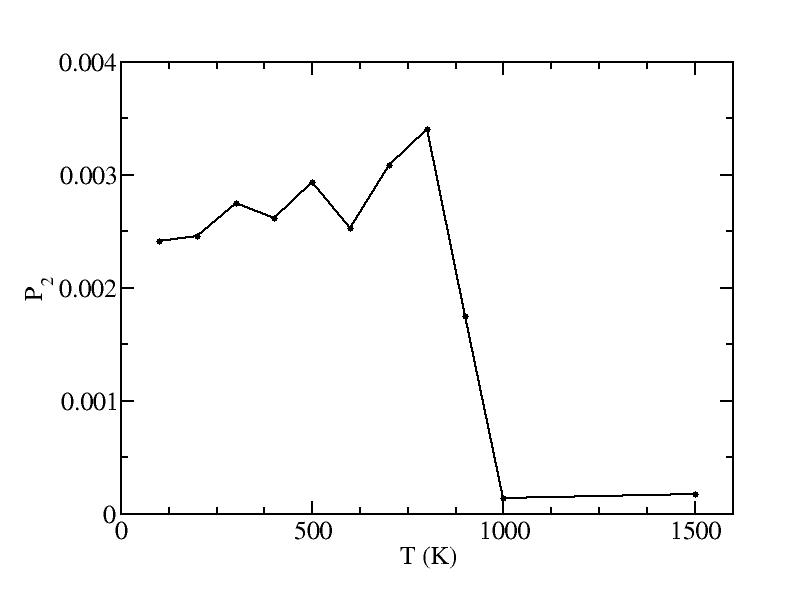
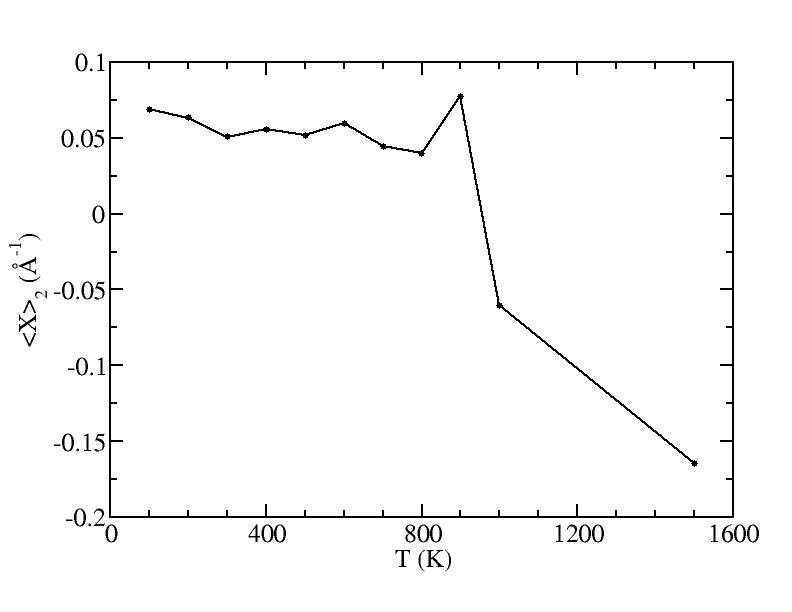
p
|
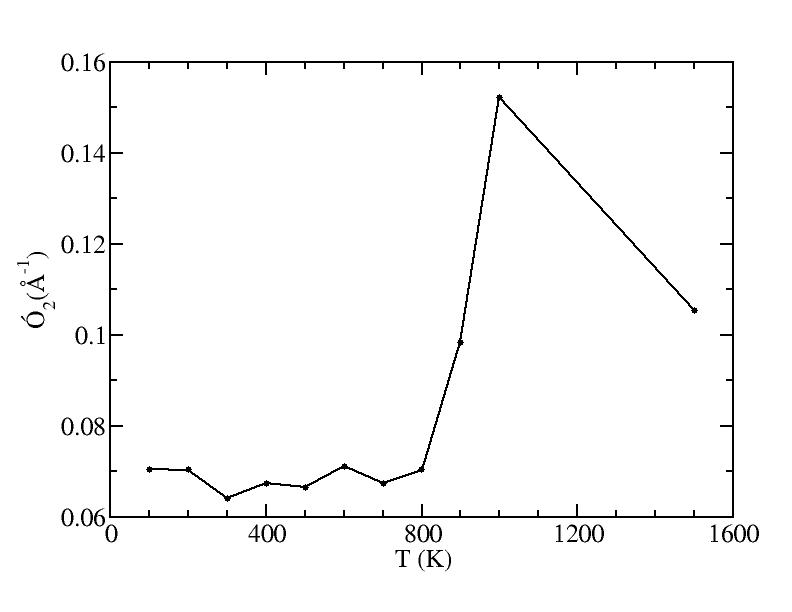
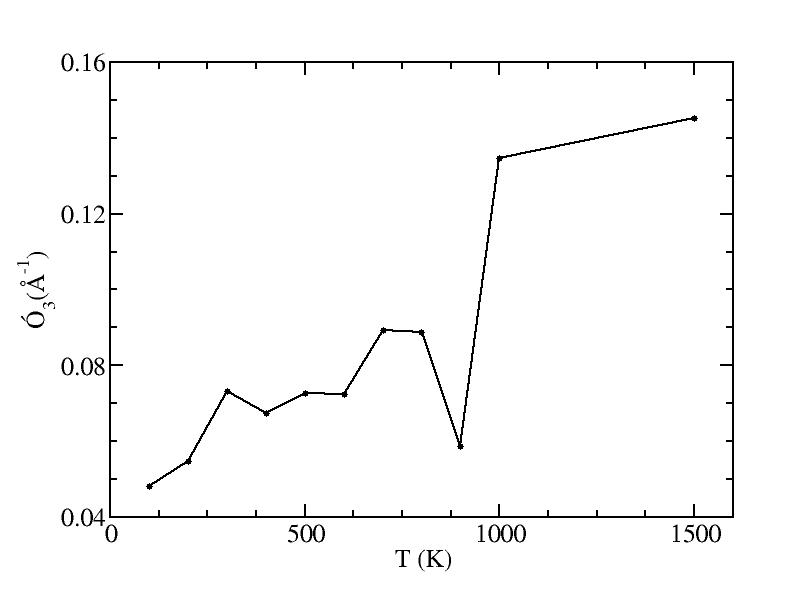
sigma
|
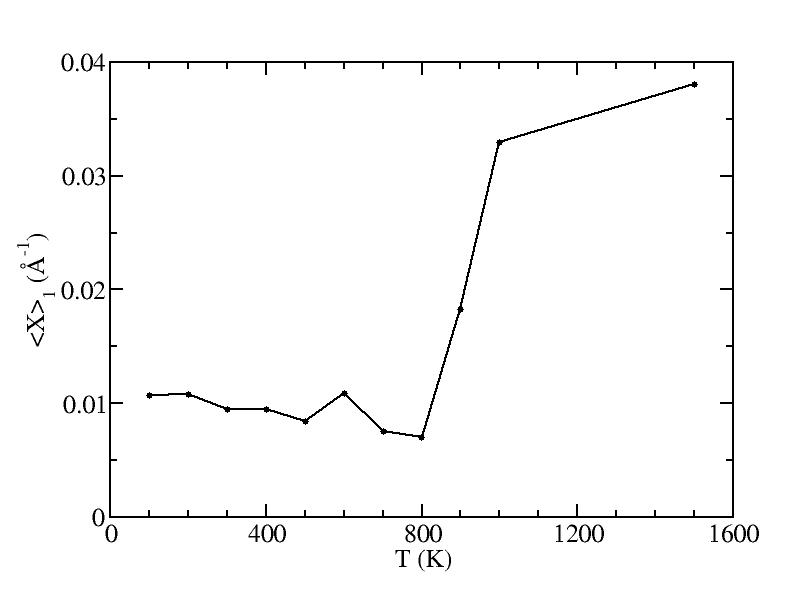
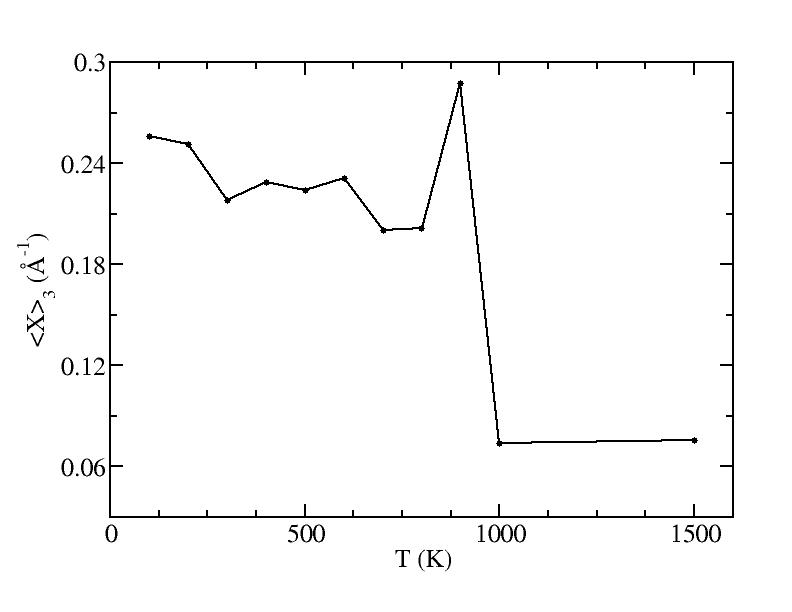
<x>
|
|
Peak 1
|
|
|
|
|
Peak 2
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Peak 3
|
 |
 |
 |
100K
200K
300K
400K
500K
600K
700K
800K
900K
1000K
1500K