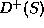 the volume expansion.
the volume expansion.
This equation has the special characteristic that it is true without
reference to the Einstein equations . That is, it is true
for any spacetime. It
is an intrinsic property of 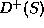 the volume expansion.
the volume expansion.
Say V is the timelike unit tangent vector of congruence of timelike geodesic (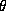 ).
).
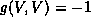 is the
acceleration of the flow line and
is the
acceleration of the flow line and 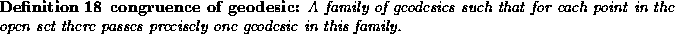 is the tensor which project a vector X of the
tangent space
is the tensor which project a vector X of the
tangent space 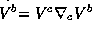 into its components in the subspace
into its components in the subspace
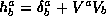 orthogonal to V.
orthogonal to V.
The Raychaudhuri equation [glo]Raychaudhuri equation say:
Where
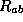
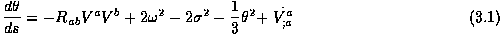 ,
,  .
.
By defining these object we emphasized the analogy with Fluids Dynamics discuss in appendix ![]() page
page ![]() .
.
A congruence of timelike geodesics has 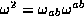 everywhere if it is zero at one point and also
everywhere if it is zero at one point and also 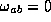 . The calculation are a lot simpler for this case.
In order to derive this equation one need to compute
. The calculation are a lot simpler for this case.
In order to derive this equation one need to compute
![]() the
derivative of the projection of the tangent vector of the
timelike curve
the
derivative of the projection of the tangent vector of the
timelike curve  (also called the Jacobi field [glo]Jacobi field because it solves the Jacobi equation [glo]Jacobi equation
(also called the Jacobi field [glo]Jacobi field because it solves the Jacobi equation [glo]Jacobi equation 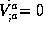 )
. Then you project and derive this equation.
By projecting it again one can find:
)
. Then you project and derive this equation.
By projecting it again one can find:
Our interest in the Raychaudhuri equation comes from the fact
that one can see the convergence of geodesic from it. It is used
in the proof of the singularity theorems . It is obvious that if 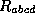 then there will be convergence of the geodesics.
then there will be convergence of the geodesics.
After some examples, like the Robertson and Walker case for dust
(see appendix ![]() page
page ![]() ), we
can now go to the null case.
), we
can now go to the null case.