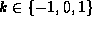 and k=0
the flat universe. This gives the system:
and k=0
the flat universe. This gives the system:
In order to simplify the computation we take the case of the
radial geodesics, this means that 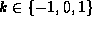 and k=0
the flat universe. This gives the system:
and k=0
the flat universe. This gives the system:
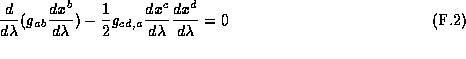
In order to find the timelike vector  we use the geodesic equations and the fact that
we use the geodesic equations and the fact that  for timelike vectors.
for timelike vectors.
This gives us
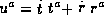
Where c is the constant equal to  (from the geodesic equation).
(from the geodesic equation).
Now we compute 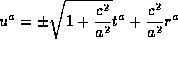 the covariant derivative of the tangent timelike vector of the geodesics.
the covariant derivative of the tangent timelike vector of the geodesics.

One can ask for what c we have 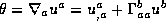 . For say c>0 one must have
. For say c>0 one must have
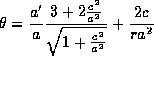
For a flat space 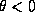 . It is not possible for this to be true if
. It is not possible for this to be true if 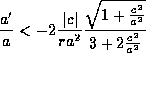 . In other words for an universe in expansion
. In other words for an universe in expansion 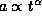 .
.
If we now take c to be negative then there exist a case of convergence for a flat space with 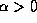 .
.