Lessons
|
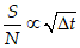 |
Instrumental sensitivity
Calculation of how much
exposure time is needed for a given observation. |
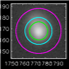 |
Calibration and reduction of images
Removing artifacts and imperfections, alignment, averaging,
and tesselation of images. |
 |
Deconvolution of images
How to make images a sharper than the seeing allows, and the
price one pays for doing so. |
 |
Basics of
observing
Quick start for learning to operate
telescope and caemera |
 |
Spectral-line imaging
Challenges in the use of narrow-band spectral-line filters in
imaging. See also the H II region long form, below. |
 |
Crowded-field stellar photometry
How to decompose the image of a dense stellar cluster into
its component stellar images. |
 |
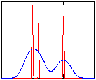
Observation of periodically-variable objects
Observing cadence, light curves, and periodograms. |
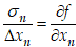 |
Uncertainties in astronomical observations
How to propagate uncertainties through the calibration and
reduction process |
 |
Pretty
astronomical pictures
With 4 hours and a few tricks in Photoshop, one can make
extremely respectable pictures at Mees. With 40-80 hours, APOD
quality. |
Other resources
|
 |
Astronomy
203
Lectures 18 (first three sections) and 19-24 pertain to
lesson 1. |
 |
H II regions: the long form
Elaboration on the short form
presented in the lesson on spectral-line imaging.
|